DICOM Router/Gateway Workflow
Very often questions are asked about DICOM Router/Gateway implementations. So this is a summary of the options.
Why Routing?
- It can allow multiple SCUs(Clients) perform composite and normalized DICOM operations on remote PACS Server.
- It can allow SCUs retrieve Images via C-GET, which is NOT supported by many PACS nowadays.
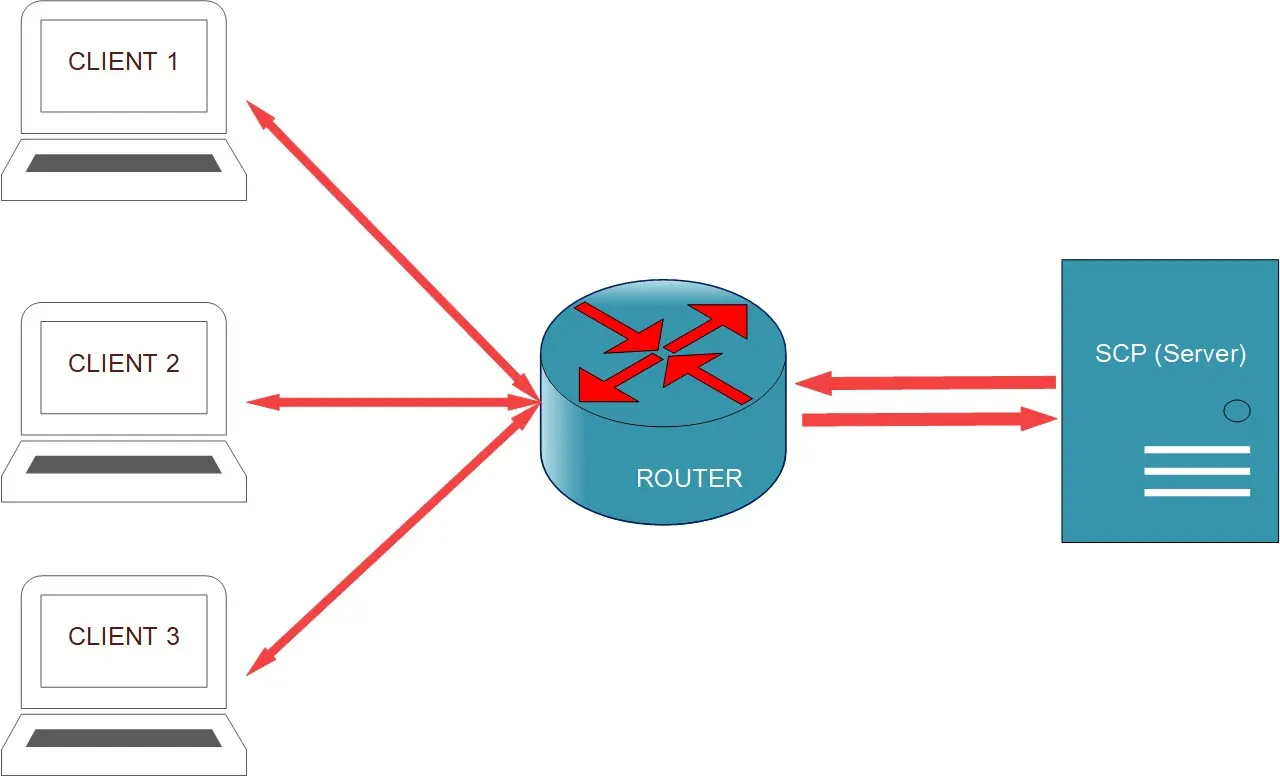
The General Work Flow
The general routing work flow is simple. It forwards every incoming requests, including all DICOM composite as well as normalized operations, and return meaningful status and results (if there is any) to the client, as shown in the following picture.
The DICOM Composite Operations
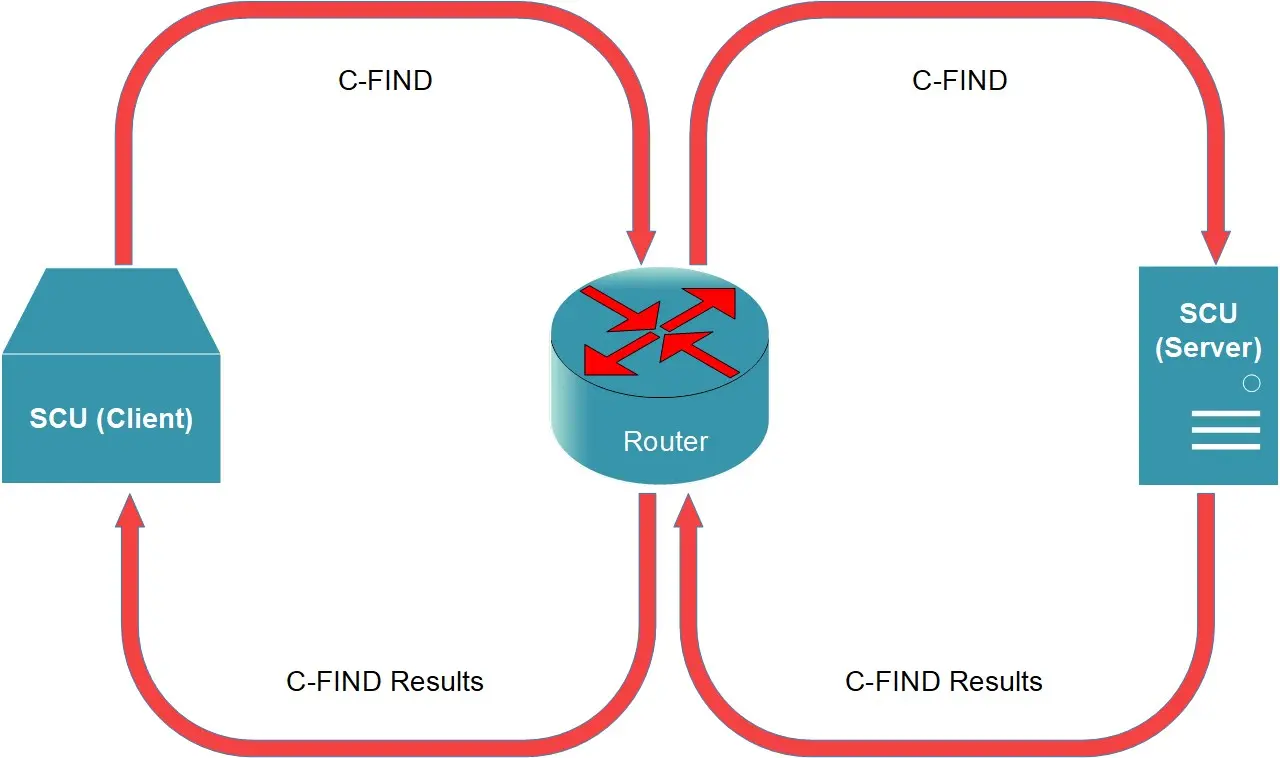
C-FIND
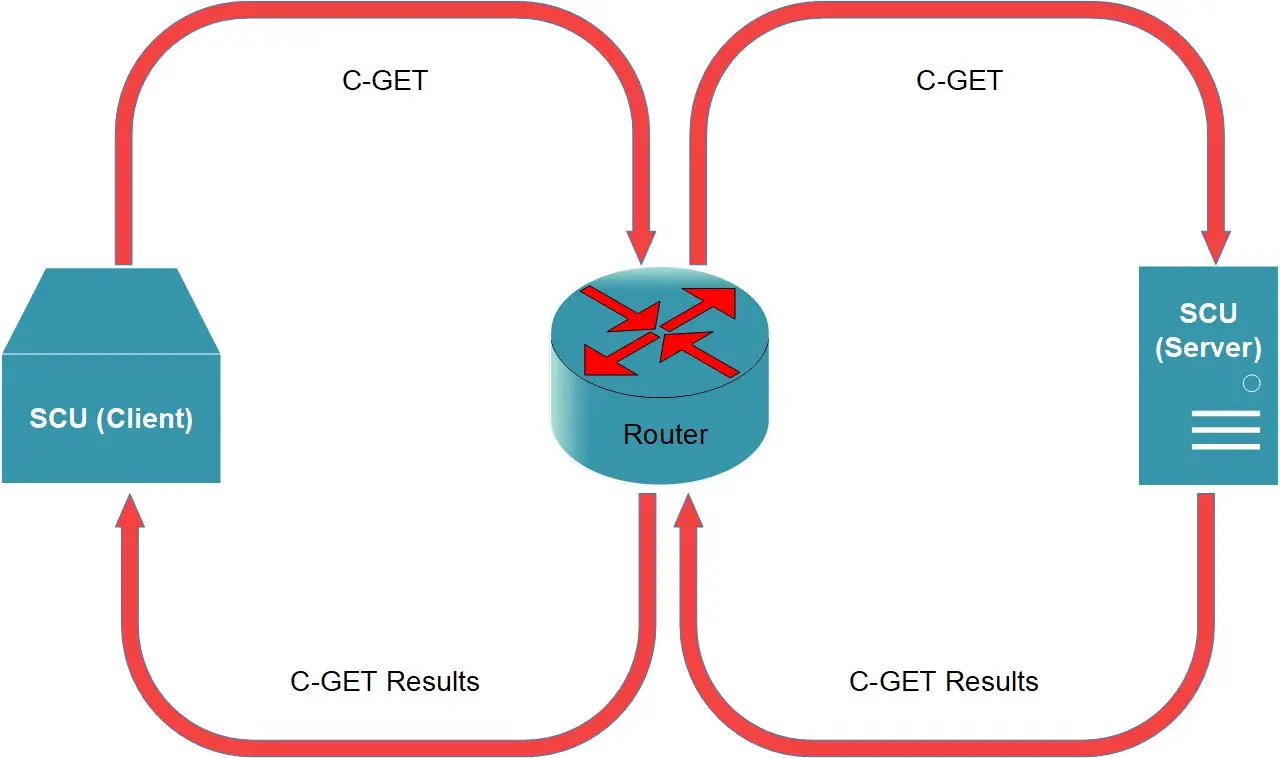
C-GET
Using C-GET to Handle Incoming C-GET Requests
Again, using C-GET to handle C-GET is simple forwarding.
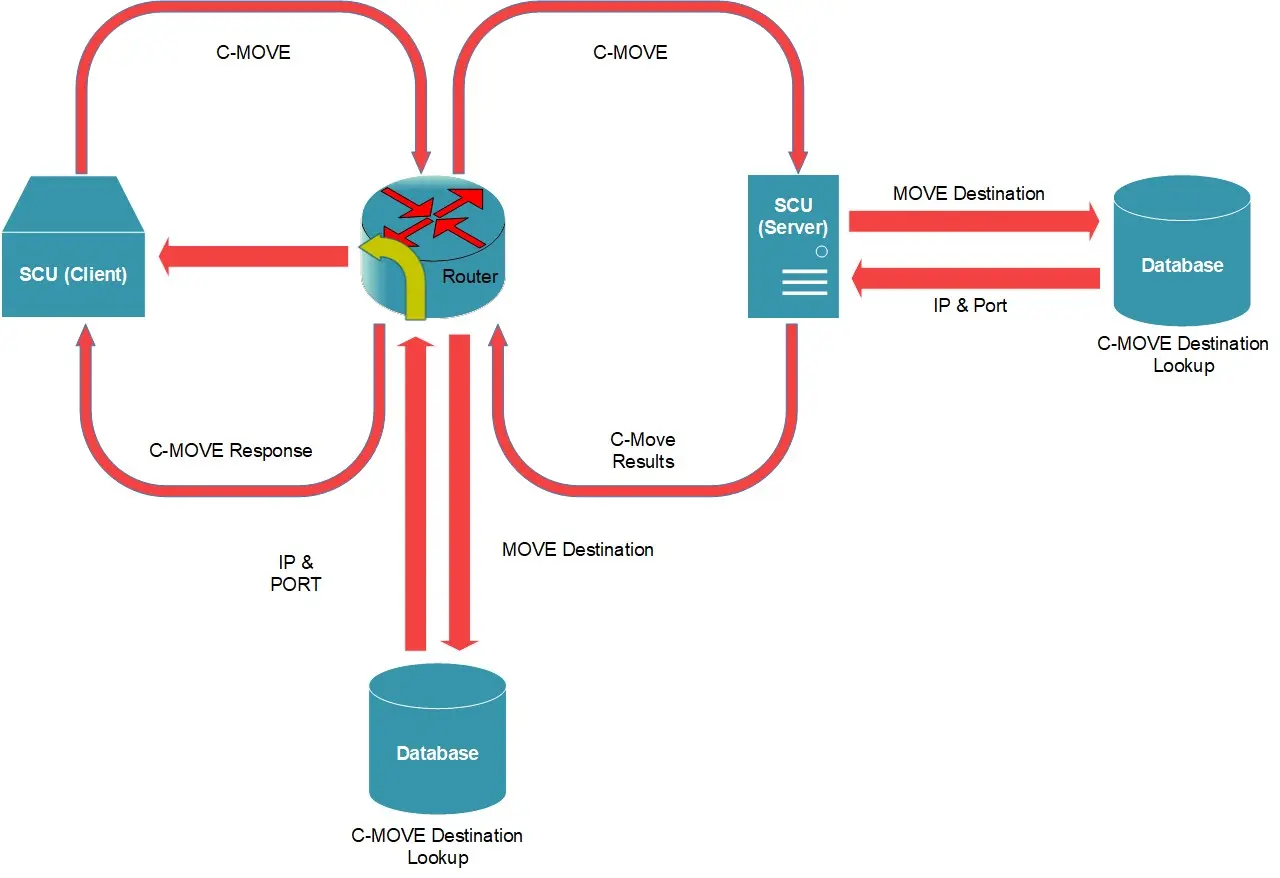
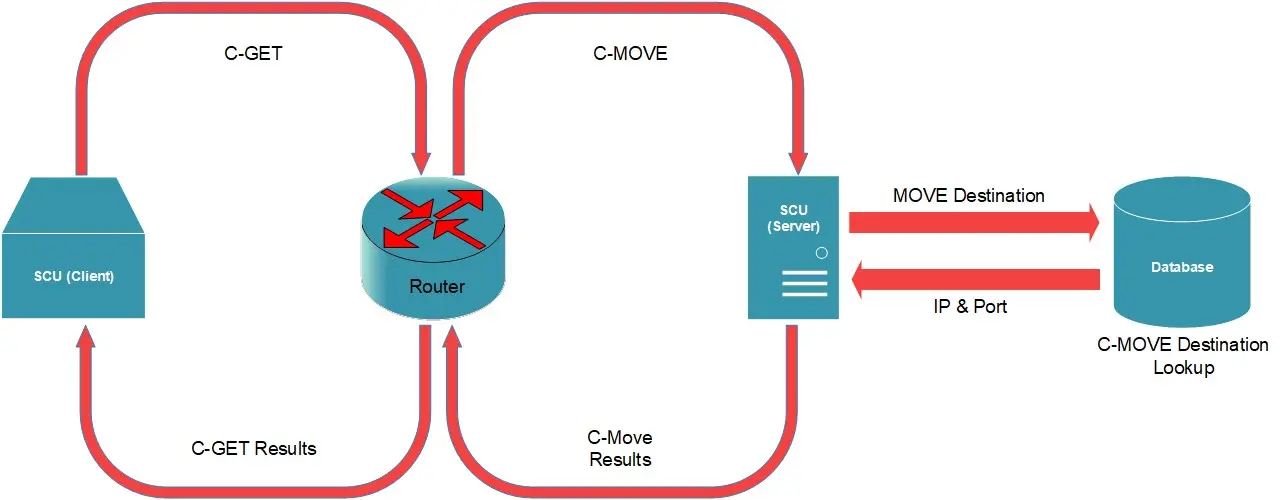
Using C-MOVE to Handle Incoming C-GET Requests
Using C-MOVE to handle C-GET is more difficult than using C-GET, due to the complex nature of C-MOVE. It requires close co-ordination between Router and Server, IE. Move Destination AET Lookup on server and router must be listening on the correct port, which is associated its AET.
C-MOVE
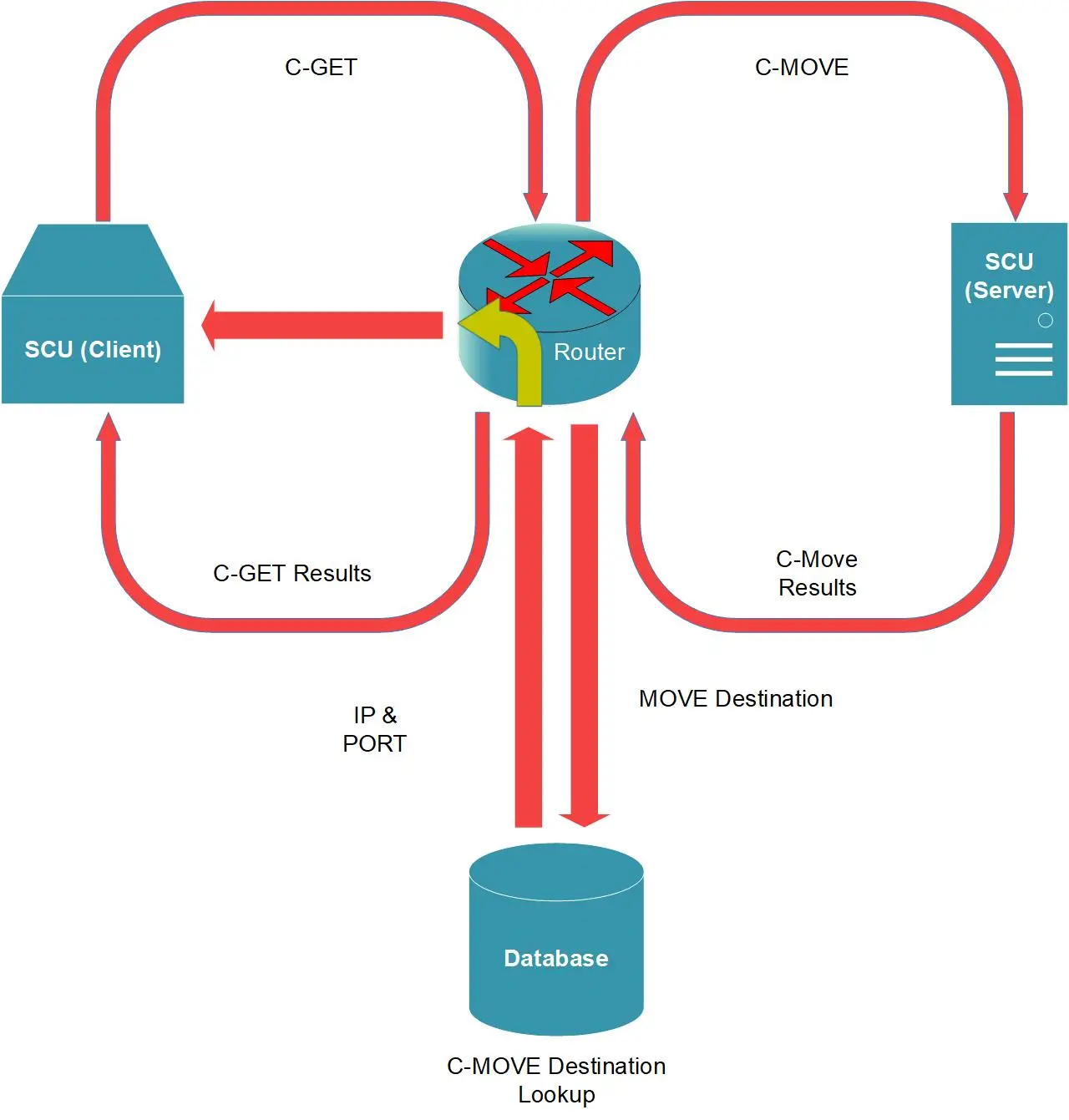
Using C-GET to Handle Incoming C-MOVE Requests
Using C-MOVE to Handle Incoming C-MOVE Requests
This is the most complex one, as it requires both Server and Router to do MOVE Destination AET lookup. Client must be listening on the correct port number associated with its AET, which is stored in Router’s AET lookup table. Router must be listening on the correct port number associated with its AET, which is stored in Server’s AET lookup table.